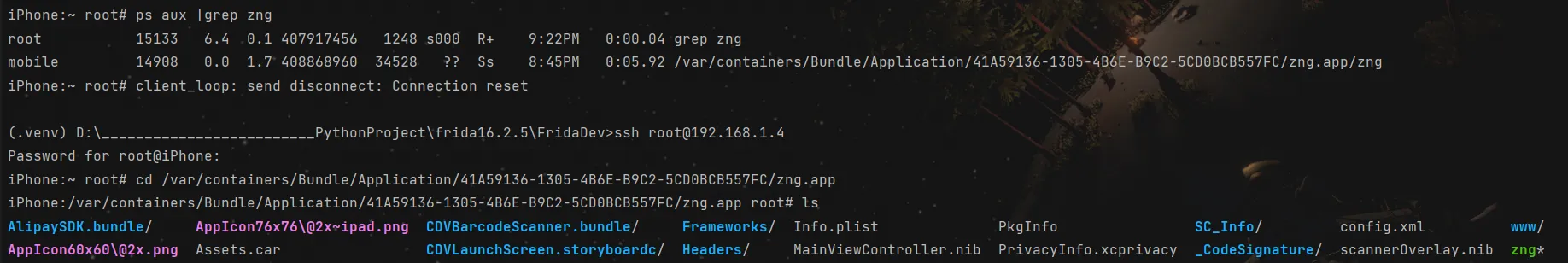
jailbreak env
ssh
The first connection will ask for your confirmation, you need to type yes.
The public key information will be saved in C:\Users\Administrator\.ssh\known_hosts.
When prompted with an “man-in-the-middle attack” warning, you can resolve it by deleting the public key inside.
Passwordless Login
Generate a public-private key pair using
ssh-keygen.Save path:
C:\Users\Administrator/.ssh/id_rsa(private key)C:\Users\Administrator/.ssh/id_rsa.pub(public key)
Copy the public key to the corresponding directory on the mobile device:
scp C:\Users\Administrator/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@ip:/tmp
Append the public key’s content from
/tmp/id_rsa.pubto.ssh/authorized_keys:- Connect to the server:
ssh root@192.168.1.4 - Create the
.sshdirectory if it doesn’t exist:mkdir .ssh - Append the key:
cat /tmp/id_rsa.pub >> .ssh/authorized_keys
- Connect to the server:
To cancel passwordless login, simply delete the
authorized_keysfile on the mobile device.
Passwordless login essentially uses the computer’s public key as a password to log in, which is why a public-private key pair must be generated first.
https://dkxuanye.cn/?cat=116 good toturials :)
WinRa1n 2.0 is a good tool :)
or use 爱斯助手(iTunes) the usb ones method
frida
frida https://frida.re/docs/ios/#with-jailbreak
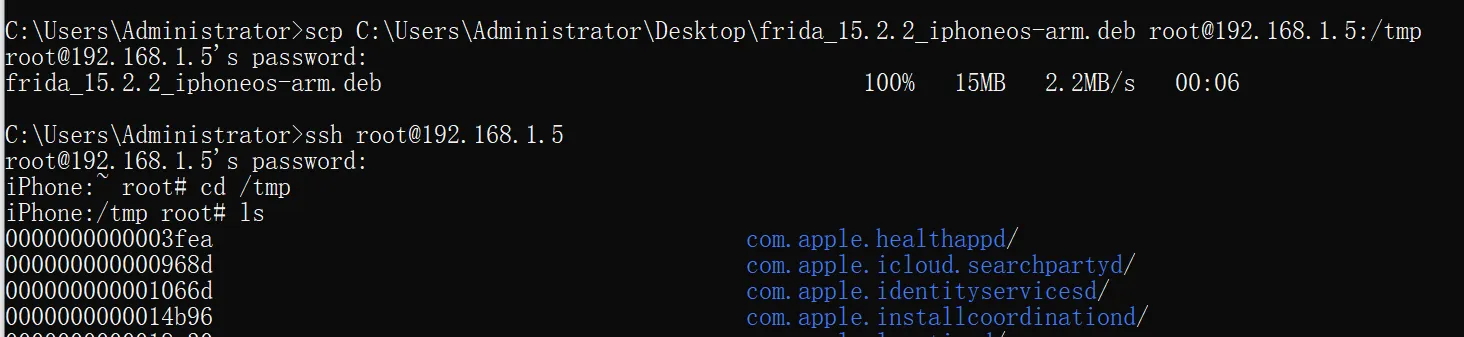
you don’t have to connect with computer via usb cab
![]()
windows can’t connect with ios via usb… it seems like that it’s drive should be changed…
but we can solve this problem by wireless remote connect
**0x00 **
We often use old iphones for jailbreaking and debugging. USB connection is really subpar; it always disconnects at crucial moments.
0x01 iPhone ssh:
frida-server -l 0.0.0.0
0x02 PC :
frida-ps -H 192.168.111.120
0x03 execute frida command
frida-trace -H 192.168.1.3:1337 -i "open*"
remember to add -H IP:Port
# listen on 127.0.0.1:27042 (the default)
$ frida-server
# listen on all interfaces
$ frida-server -l 0.0.0.0
# listen on a specific interface
$ frida-server -l 192.168.1.3
# listen on a specific interface and port
$ frida-server -l 192.168.1.3:1337
# connect to specific IP
$ frida-trace -H 192.168.1.3 -i "open*"
# connect to specific IP/port
$ frida-trace -H 192.168.1.3:1337 -i "open*"
cyz1nappleID
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/74111266/failed-to-spawn-unable-to-find-process-with-name
Without the
-Uand-Dparameter Frida tries to find and attach to a process on your local PC instead of your Android device.Considering everything I would use the following command:
frida-trace -U -N <app-package-name>
https://book.crifan.org/books/reverse_debug_frida/website/use_frida/frida_cli/debug_target.html
install shit


framework like lsp: theos
install a specific version of frida
https://github.com/frida/frida/releases?q=14.2.18&expanded=true. choose frida_14.2.18_iphoneos-arm.deb
use scp command to move this file from pc to ipone

cd /tmp
dpkg -i frida_xxxxx
ps aux |grep frida
on your PC, install corresponding frida and frida-tools https://github.com/thelicato/frida-compatibility-matrix
install objection
recommend version:
pip install frida==14.2.18
pip install frida-tools==9.2.5
pip install objection==1.11.0 (latest)

install trollstore
https://ios.cfw.guide/installing-trollstore/
Ch1ne5e user remember to open VPN, it need to download kernel.
Charles
- download a certificate on ios
charlesproxy.com/getssl
chls.pro/ssl
- click click in iphone
env detection
sometimes, an application can bypass system proxy, so we can use a VPN to force it to go through our proxy. Here we use Shadowrocket
open charles to see the port and IP
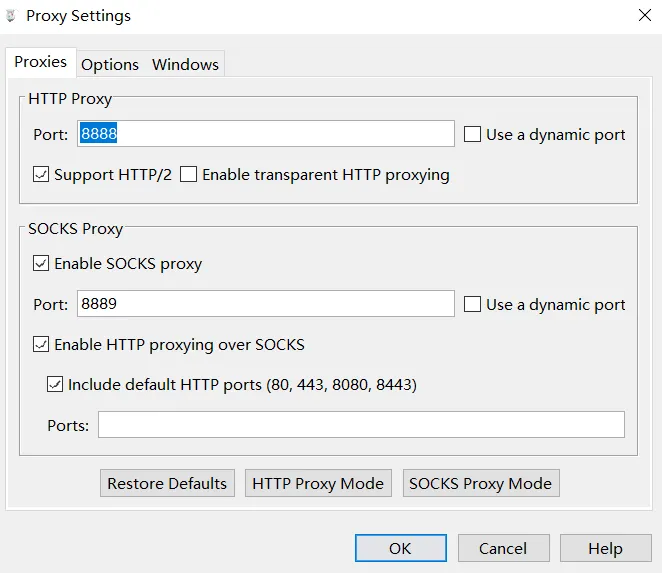
open shadowrocket, type Socks5 server 192.168.1.6 port8889. Change Global Routing to ‘Proxy’2
proxy
method 1: hook [r0capture][https://github.com/r0ysue/r0capture] :+1: :star2:
Basic Universal Hooking for Packet Capture
HTTPS requests are essentially HTTP + SSL/TLS. There are generally two situations for SSL: either using the system’s SSL library or a custom one. The system SSL library is called libboringssl.dylib. You can get plaintext data by hooking SSL_read and SSL_write.
Custom SSL libraries are more common in applications like WebView, Flutter, or those that have compiled their own open-source BoringSSL.
For the third scenario (custom SSL libraries), you can generally find the corresponding SSL_read and SSL_write within the relevant dynamic library (.dylib) and hook them.
var ssl_write = Module.findExportByName("libboringssl.dylib", "SSL_write");
Interceptor.attach(ssl_write, {
onEnter: function (args) {
console.log("=========================================");
console.log("Current Thread Id: ", Process.getCurrentThreadId(), " | ssl_write onEnter | input length: ", args[2].toInt32());
console.log(hexdump(args[1], {
length: args[2].toInt32()
}));
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
}
});
var ssl_read = Module.findExportByName("libboringssl.dylib", "SSL_read");
Interceptor.attach(ssl_read, {
onEnter: function(args) {
this.buf = args[1];
this.len = args[2].toInt32();
},
onLeave: function(retval) {
if (retval.toInt32() > 0) {
console.log("=========================================");
console.log("Current Thread Id: ", Process.getCurrentThreadId(), " | ssl_read onLeave | output length: ", retval.toInt32());
console.log(hexdump(this.buf, {
length: retval.toInt32()
}));
}
}
});
// frida -U -N com.dodonew.member.overseas -l hook.js
but i think its totally fucked up XD
method 2:
this is a proxy detection function
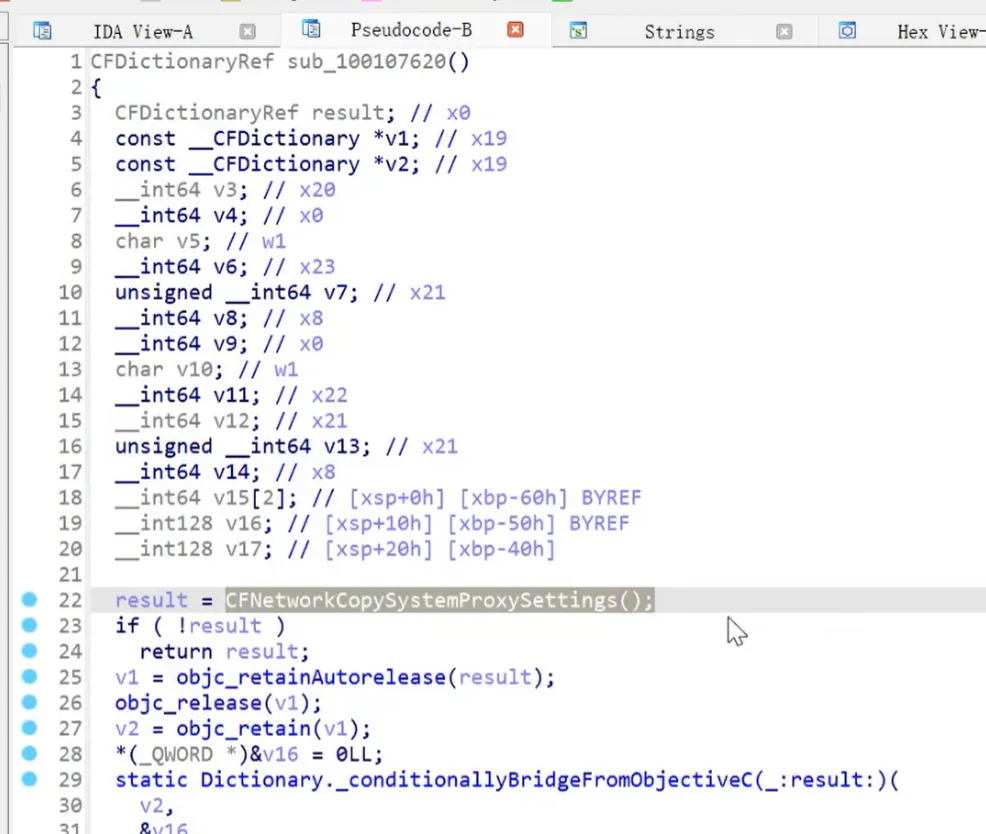

see imp, two posibility: 1. import from system 2. import from a dynamic library. heres its hook script, return 0
var _imports = Process.findModuleByName("tredian").enumerateImports();
var _CFNetworkCopySystemProxySettings = null;
for (var i = 0; i < _imports.length; i++) {
if (_imports[i].name.indexOf("CFNetworkCopySystemProxySettings") != -1) {
console.log(_imports[i].name, _imports[i].address);
_CFNetworkCopySystemProxySettings = _imports[i].address;
}
}
if (_CFNetworkCopySystemProxySettings) {
Interceptor.attach(_CFNetworkCopySystemProxySettings, {
onEnter: function(agrgs) {
// InvocationArguments
},
onLeave: function(retval) {
// InvocationReturnValue
console.log("retval: ", ObjC.Object(retval));
retval.replace(0);
}
});
}
// frida-ps -Uai
// frida -U -f maihan.tredian -l hook.js
in a normal environment, _ _SCOPED _ _only has en0, but when you open a VPN, utun3 was added.
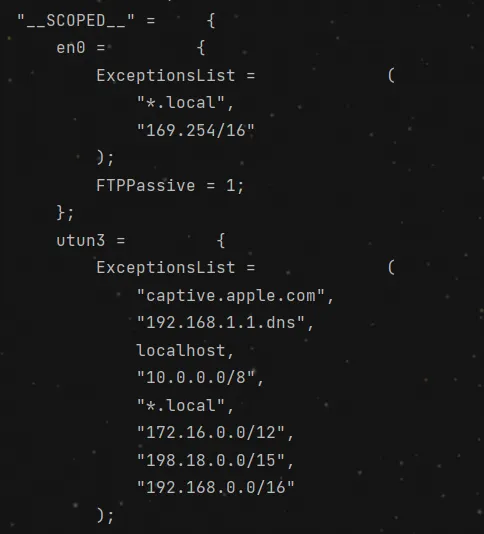
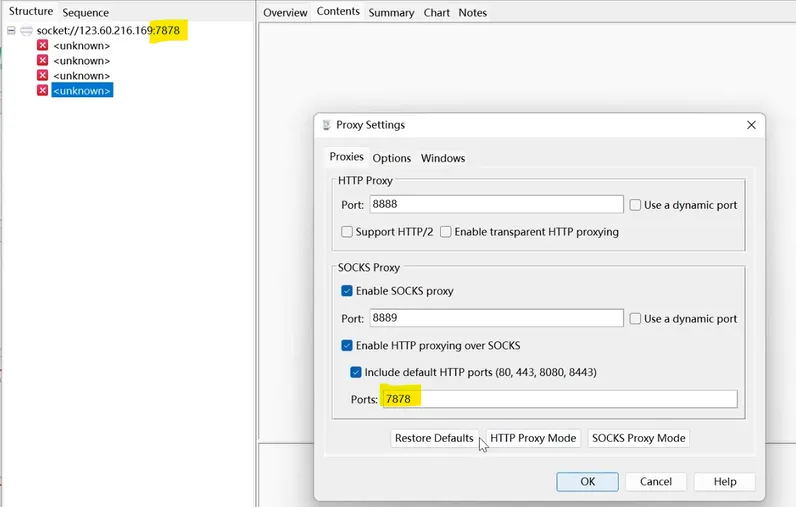
off-standard port.
weex
once launching a VPN, the app can’t work well. notice that its port isn’t normal, so add this port to Ports
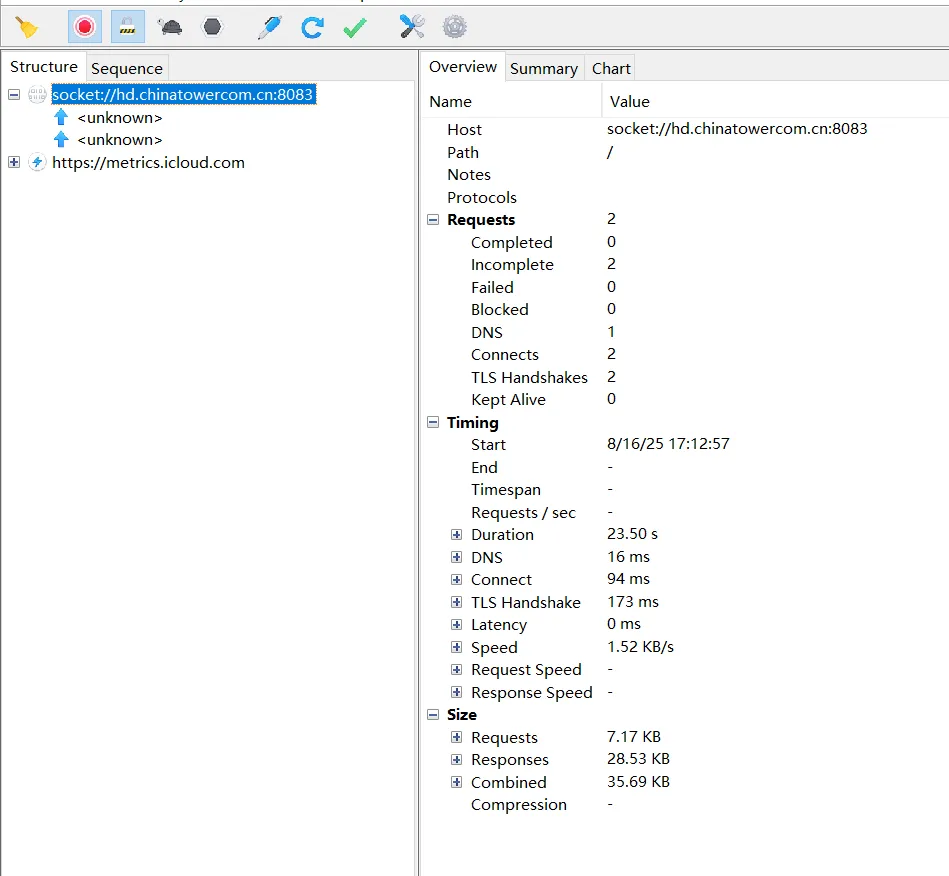
find the place that seems like the place where it sent a post. it called weex
id __cdecl -[WXStreamModule _buildRequestWithOptions:callbackRsp:](WXStreamModule *self, SEL a2, id a3, id a4)
{
id v6; // x27
id v7; // x28
void *v8; // x0
id v9; // x23
void *v10; // x24
void *v11; // x0
id v12; // x21
void *v13; // x0
id v14; // x25
void *v15; // x0
id v16; // x26
void *v17; // x0
id v18; // x19
id v19; // x27
id v20; // x22
__int64 v21; // x28
void *v22; // x0
id v23; // x21
void *v24; // x0
id v25; // x22
void *v26; // x0
id v27; // x22
id v28; // x26
void *v29; // x0
id v30; // x21
void *v31; // x0
id v32; // x21
void *v33; // x0
id v34; // x0
void *v35; // x23
id v36; // x24
char v37; // w25
void *v38; // x0
id v39; // x22
void *v40; // x0
id v41; // x23
double v42; // d0
void *v43; // x0
id v44; // x23
void *v45; // x0
id v46; // x22
void *v47; // x0
__CFString *v48; // x19
void *v49; // x0
id v50; // x23
void *v51; // x0
id v52; // x25
void *v53; // x0
id v54; // x25
void *v55; // x0
id v56; // x25
float v57; // s0
void *v58; // x0
id v59; // x25
void *v60; // x0
id v61; // x25
__int64 v62; // x0
__int64 v63; // x27
__int64 v64; // x21
__int64 i; // x19
void *v66; // x0
void *v67; // x0
id v68; // x24
void *v69; // x0
id v70; // x23
void *v71; // x0
id v72; // x24
int v73; // w26
void *v74; // x0
id v75; // x0
void *v76; // x27
void *v77; // x0
id v78; // x26
int v79; // w23
void *v80; // x0
id v81; // x24
void *v82; // x0
id v83; // x23
void *v84; // x0
void *v85; // x0
id v86; // x23
int v87; // w24
void *v88; // x0
void *v89; // x0
void *v90; // x0
id v91; // x24
void *v92; // x0
id v93; // x23
void *v94; // x0
id v95; // x23
id v97; // [xsp+170h] [xbp+10h]
void *v98; // [xsp+178h] [xbp+18h]
__CFString *v99; // [xsp+180h] [xbp+20h]
id v100; // [xsp+188h] [xbp+28h]
WXStreamModule *v101; // [xsp+198h] [xbp+38h]
id v102; // [xsp+198h] [xbp+38h]
id v103; // [xsp+1E8h] [xbp+88h]
v6 = objc_retain(a3);
v7 = objc_retain(a4);
v8 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v6);
v9 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v8);
sub_1014BB4E0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSString);
if ( (sub_1014DE220(v9) & 1) != 0 )
{
v10 = (void *)sub_1014BF280(v9);
v11 = (void *)sub_1014D4FC0(&OBJC_CLASS___WXSDKEngine);
v12 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v11);
v101 = self;
if ( (unsigned int)sub_1014F5DA0() )
{
v13 = (void *)-[DCUniComponent uniInstance]_0(self);
v14 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v13);
v15 = (void *)sub_1014F6B40(v12);
v16 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v15);
v17 = (void *)sub_1014AF780();
v18 = v6;
v19 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v17);
v20 = v7;
v21 = sub_1014BF280(v19);
objc_release(v10);
v22 = v19;
v6 = v18;
objc_release(v22);
objc_release(v16);
objc_release(v14);
v10 = (void *)v21;
v7 = v20;
}
objc_release(v12);
v23 = objc_retain(v10);
objc_release(v9);
if ( !v6 || (unsigned int)sub_1014DD000(&OBJC_CLASS___WXUtility) )
{
v24 = (void *)sub_1014E8EE0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSNumber);
v25 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v24);
sub_10150C640(v7);
objc_release(v25);
v26 = (void *)sub_1014E8E60(&OBJC_CLASS___NSNumber);
v27 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v26);
sub_10150C640(v7);
objc_release(v27);
v28 = 0LL;
LABEL_41:
objc_release(v23);
goto LABEL_42;
}
v33 = (void *)-[DCUniComponent uniInstance]_0(v101);
v34 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v33);
if ( v34 )
{
v35 = v34;
v36 = objc_loadWeakRetained((id *)&v101->weexInstance);
v37 = sub_1014DE1C0();
objc_release(v36);
objc_release(v35);
if ( (v37 & 1) == 0 )
{
v38 = (void *)-[DCUniComponent uniInstance]_0(v101);
v39 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v38);
v40 = (void *)sub_1014ECC80();
v41 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v40);
v42 = sub_1014CECA0();
sub_101504EA0(v41, v42 + 1.0);
objc_release(v41);
objc_release(v39);
}
}
v43 = (void *)sub_1014ABE60(&OBJC_CLASS___NSURL);
v44 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v43);
v45 = (void *)sub_1014F54C0(&OBJC_CLASS___WXResourceRequest);
v46 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v45);
objc_release(v44);
v47 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v6);
v48 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v47);
if ( (unsigned int)sub_1014DD000(&OBJC_CLASS___WXUtility) )
{
objc_release(v48);
v48 = CFSTR("GET");
}
sub_101505500(v46);
v49 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v6);
v50 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v49);
sub_1014BB4E0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSString);
if ( (unsigned int)sub_1014DE220(v50) )
{
if ( v50 )
{
v51 = (void *)sub_1014E48C0(v50);
v52 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v51);
sub_10150C640(v7);
objc_release(v52);
}
else
{
sub_10150C640(v7);
}
}
v98 = v50;
v99 = v48;
v100 = v23;
v53 = (void *)sub_101524720(v6);
v54 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v53);
objc_release(v54);
if ( v54 )
{
v55 = (void *)sub_101524720(v6);
v56 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v55);
v57 = sub_1014CDEC0();
sub_101514B20(v46, (float)(v57 / 1000.0));
objc_release(v56);
}
v58 = (void *)sub_1014C1660(&OBJC_CLASS___PTUserAgentUtil);
v59 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v58);
sub_101516420(v46);
objc_release(v59);
v102 = v6;
v60 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v6);
v61 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v60);
v62 = ((__int64 (*)(void))sub_1014BF720)();
if ( v62 )
{
v63 = v62;
v64 = MEMORY[0];
do
{
for ( i = 0LL; i != v63; ++i )
{
if ( MEMORY[0] != v64 )
objc_enumerationMutation(v61);
v66 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v61);
v97 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v66);
v67 = (void *)sub_10151D280(&OBJC_CLASS___NSString);
v68 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v67);
objc_release(v97);
sub_101516780(v46);
objc_release(v68);
}
v63 = sub_1014BF720(v61);
}
while ( v63 );
}
v6 = v102;
v69 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v102);
v70 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v69);
objc_release(v70);
v23 = v100;
if ( v70 )
{
v71 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v102);
v72 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v71);
sub_1014BB4E0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSString);
v73 = sub_1014DE220(v72);
objc_release(v72);
v74 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v102);
v75 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v74);
v76 = v75;
if ( v73 )
{
v77 = (void *)sub_1014C20A0(v75);
v78 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v77);
objc_release(v76);
v6 = v102;
if ( !v78 )
{
LABEL_39:
v92 = (void *)sub_1014E8EE0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSNumber);
v93 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v92);
sub_10150C640(v7);
objc_release(v93);
v94 = (void *)sub_1014E8E60(&OBJC_CLASS___NSNumber);
v95 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v94);
sub_10150C640(v7);
objc_release(v95);
v28 = 0LL;
goto LABEL_40;
}
}
else
{
sub_1014BB4E0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSDictionary);
v79 = sub_1014DE220(v76);
objc_release(v76);
if ( v79 )
{
v6 = v102;
v80 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v102);
v81 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v80);
v82 = (void *)sub_1014AAC20(&OBJC_CLASS___WXUtility);
v83 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v82);
v84 = (void *)((__int64 (*)(void))sub_1014C20A0)();
v78 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v84);
objc_release(v83);
objc_release(v81);
if ( !v78 )
goto LABEL_39;
}
else
{
v6 = v102;
v85 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v102);
v86 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v85);
sub_1014BB4E0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSData);
v87 = sub_1014DE220(v86);
objc_release(v86);
if ( !v87 )
goto LABEL_39;
v88 = (void *)-[APKKeychainBindings stringForKey:]_0(v102);
v78 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v88);
if ( !v78 )
goto LABEL_39;
}
}
sub_101505460(v46);
objc_release(v78);
}
v89 = (void *)sub_1014E8EE0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSNumber);
v103 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v89);
v90 = (void *)sub_1014C6480(&OBJC_CLASS___NSDictionary);
v91 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v90);
sub_10150C640(v7);
objc_release(v91);
objc_release(v103);
v28 = objc_retain(v46);
LABEL_40:
objc_release(v61);
objc_release(v98);
objc_release(v99);
objc_release(v46);
goto LABEL_41;
}
if ( v7 )
{
v29 = (void *)sub_1014E8EE0(&OBJC_CLASS___NSNumber);
v30 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v29);
sub_10150C640(v7);
objc_release(v30);
v31 = (void *)sub_1014E8E60(&OBJC_CLASS___NSNumber);
v32 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v31);
sub_10150C640(v7);
objc_release(v32);
}
v28 = 0LL;
v23 = v9;
LABEL_42:
objc_release(v23);
objc_release(v7);
objc_release(v6);
return objc_autoreleaseReturnValue(v28);
}
hook it
defineHandler({
onEnter(log, args, state) {
var dic = ObjC.Object(args[2]);
log(`-[WXStreamModule _buildRequestWithOptions:${args[2]} callbackRsp:${args[3]}]`);
log('body', dic.objectForKey_('body'));
},
onLeave(log, retval, state) {
}
});
// frida-trace -U -f com.chinatower.towerEle4 -m "-[WXStreamModule _buildRequestWithOptions:callbackRsp:]"
certificate verification
find the p12 certificate at here. double click it on windows if it can show something means that its not encrypted
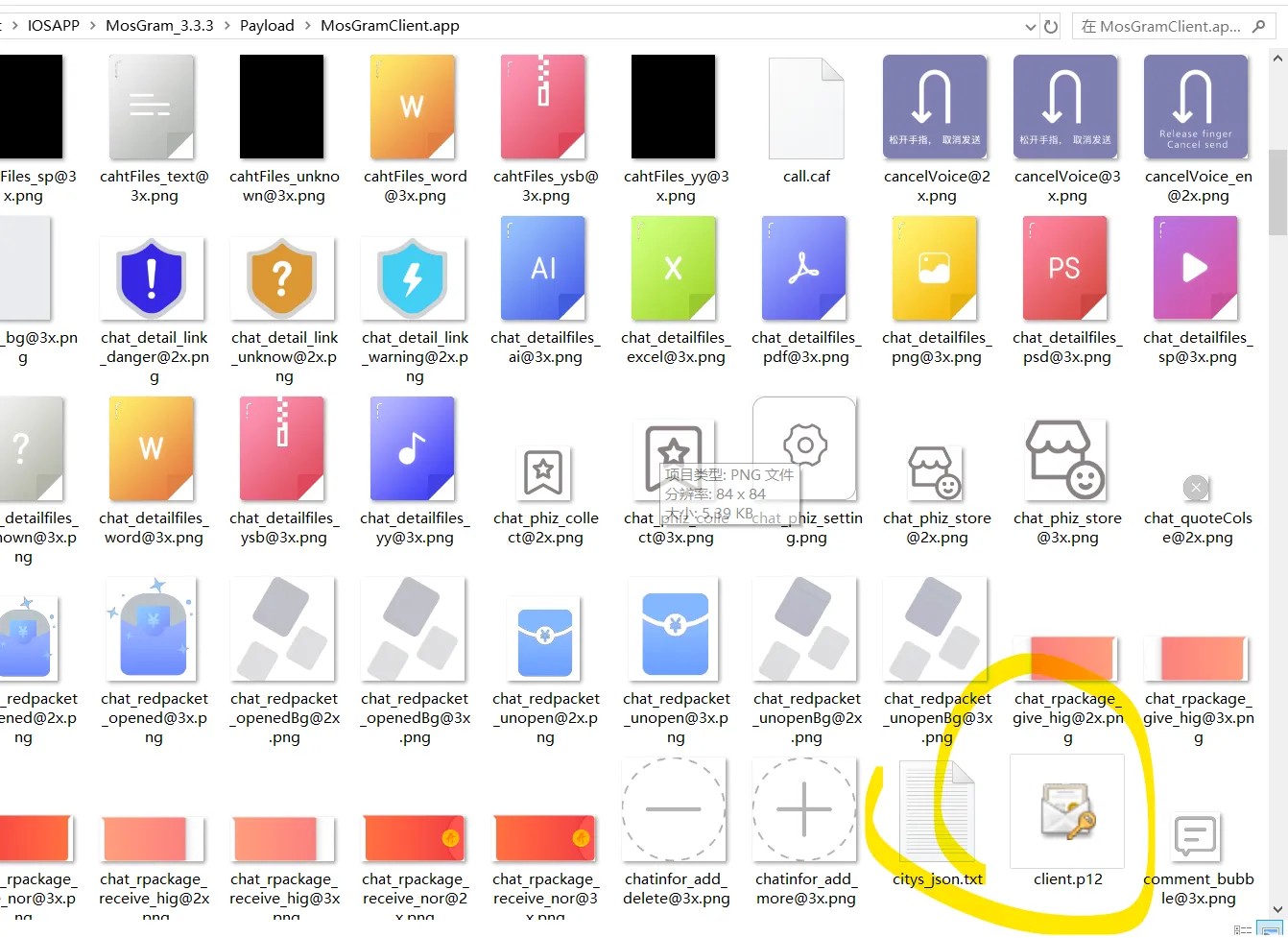
in the next step, find the password. * means find all functions contain pathForResource
defineHandler({
onEnter(log, args, state) {
// console.log('NSBundle pathForResource called from:\n' +
// Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE)
// .map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join('\n') + '\n');
log(`-[NSBundle pathForResource:${ObjC.Object(args[2])} ofType:${ObjC.Object(args[3])}]`);
},
onLeave(log, retval, state) {
}
});
// frida-trace -U -N com.mos.gram -m "-[NSBundle pathForResource*]"


open IDA and jump to address 0x1001837ec
id __cdecl -[MOSGRAM_ATHTTPSessionManager credential](MOSGRAM_ATHTTPSessionManager *self, SEL a2)
{
void *v3; // x0
id v4; // x20
void *v5; // x0
id v6; // x0
void *v7; // x20
void *v8; // x0
id v9; // x19
id v10; // x21
SecCertificateRef v12; // [xsp+0h] [xbp-30h] BYREF
SecIdentityRef v13; // [xsp+8h] [xbp-28h]
v3 = (void *)sub_100BF2D60(&OBJC_CLASS___NSBundle, a2);
v4 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v3);
v5 = (void *)sub_100C0C0C0();
objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v5);
objc_release(v4);
v6 = objc_alloc((Class)&OBJC_CLASS___NSData);
v7 = (void *)sub_100BE4E40(v6);
v13 = 0LL;
sub_100BF9C60(self);
v12 = 0LL;
SecIdentityCopyCertificate(v13, &v12);
v8 = (void *)sub_100BCF700(&OBJC_CLASS___NSURLCredential);
v9 = objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(v8);
objc_release(v7);
objc_release(v10);
return objc_autoreleaseReturnValue(v9);
}
in NSData, initWithContentsOfFile is used to save a content to NSData, given a path.
id __fastcall sub_100BE4E40(void *a1)
{
return _objc_msgSend(a1, "initWithContentsOfFile:");
}
id __fastcall sub_100BF9C60(void *a1)
{
return _objc_msgSend(a1, "mosGramM_extractIdentity:toIdentity:");
}
mosGramM_extractIdentity:toIdentity: is sus, search this function

int __cdecl -[MOSGRAM_ATHTTPSessionManager mosGramM_extractIdentity:toIdentity:](MOSGRAM_ATHTTPSessionManager *self, SEL a2, __CFData *a3, __SecIdentity **a4)
{
const __CFDictionary *v5; // x20
CFDataRef v6; // x21
int v7; // w21
const __CFDictionary *v8; // x0
CFArrayRef v10; // [xsp+0h] [xbp-40h] BYREF
__CFString *v11; // [xsp+8h] [xbp-38h] BYREF
CFStringRef v12; // [xsp+10h] [xbp-30h] BYREF
v11 = CFSTR("111111");
v12 = kSecImportExportPassphrase;
v5 = CFDictionaryCreate(0LL, (const void **)&v12, (const void **)&v11, 1LL, 0LL, 0LL);
v10 = CFArrayCreate(0LL, 0LL, 0LL, 0LL);
v7 = SecPKCS12Import(v6, v5, &v10);
if ( !v7 )
{
v8 = (const __CFDictionary *)CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(v10, 0LL);
*a4 = (__SecIdentity *)CFDictionaryGetValue(v8, kSecImportItemIdentity);
}
if ( v5 )
CFRelease(v5);
return v7;
}
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/security/secpkcs12import(::_:)

compare two script we can guess 111111 is the secret. Open Charles.

jailbreak
if([[UIApplication sharedApplication] canOpenURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"cydia://package/com.avl.com"]])
{
return YES;
}
if([[UIApplication sharedApplication] canOpenURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"cydia://package/com.example.package"]])
{
return YES;
}
defineHandler({
onEnter (log, args, state) {
var URLName = ObjC.Object(args[2]);
if (URLName.containsString_ ("http:") || URLName.containsString_ ("https:") || URLName.containsString_ ("file:")) {
} else {
if (URLName.containsString_ ("://")) {
log("[- NSURL URLWithString:]" + URLName);
args[2] = ObjC.classes.NSString.stringWithString_ ("xxxxxx://");
}
}
},
});
// frida-trace -U -f com.gemd.iting -m "+[NSURL URLWithString:]"
BOOL fileExist(NSString* path)
{
NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
BOOL isDirectory = NO;
if([fileManager fileExistsAtPath:path isDirectory:&isDirectory]){
return YES;
}
return NO;
}
BOOL directoryExist(NSString* path)
{
NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
BOOL isDirectory = YES;
if([fileManager fileExistsAtPath:path isDirectory:&isDirectory]){
return YES;
}
return NO;
}
BOOL canOpen(NSString* path)
{
FILE *file = fopen([path UTF8String], "r");
if(file==nil){
return fileExist(path) || directoryExist(path);
}
fclose(file);
return YES;
}
NSArray* checks = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:@"/Application/Cydia.app",
@"/Library/MobileSubstrate/MobileSubstrate.dylib",
@"/bin/bash",
@"/usr/sbin/sshd",
@"/etc/apt",
@"/usr/bin/ssh",
@"/private/var/lib/apt",
@"/private/var/lib/cydia",
@"/private/var/tmp/cydia.log",
@"/Applications/WinterBoard.app",
@"/var/lib/cydia",
@"/private/etc/dpkg/origins/debian",
@"/bin.sh",
@"/private/etc/apt",
@"/etc/ssh/sshd_config",
@"/private/etc/ssh/sshd_config",
@"/Applications/SBSetttings.app",
@"/private/var/mobileLibrary/SBSettingsThemes/",
@"/private/var/stash",
@"/usr/libexec/sftp-server",
@"/usr/libexec/cydia/",
@"/usr/sbin/frida-server",
@"/usr/bin/cycript",
@"/usr/local/bin/cycript",
@"/usr/lib/libcycript.dylib",
@"/System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.saurik.Cydia.Startup.plist",
@"/System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.ikey.bbot.plist",
@"/Applications/FakeCarrier.app",
@"/Library/MobileSubstrate/DynamicLibraries/Veency.plist",
@"/Library/MobileSubstrate/DynamicLibraries/LiveClock.plist",
@"/usr/libexec/ssh-keysign",
@"/usr/libexec/sftp-server",
@"/Applications/blackra1n.app",
@"/Applications/IntelliScreen.app",
@"/Applications/Snoop-itConfig.app"
@"/var/lib/dpkg/info", nil];
//Check installed app
for(NSString* check in checks)
{
if(canOpen(check))
{
return YES;
}
}
defineHandler({
onEnter(log, args, state) {
var fileName = ObjC.Object(args[2]);
if (fileName.containsString_("apt") ||
fileName.containsString_("MobileSubstrate") ||
fileName.containsString_("Cydia") ||
fileName.containsString_("bash") ||
fileName.containsString_("ssh") ||
fileName.containsString_("/bin/sh") ||
fileName.containsString_("Applications") ||
fileName.containsString_("/bin/su") ||
fileName.containsString_("dpkg")) {
console.log('fileExistsAtPath called from:\n' +
Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE)
.map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join('\n') + '\n');
args[2] = ObjC.classes.NSString.stringWithString_("/xxxxxx");
log('[-NSFileManager fileExistsAtPath: ${fileName}]');
}
},
onLeave(log, retval, state) {
}
});
// frida-trace -U -f com.gemd.iting -m "-[NSFileManager fileExistsAtPath:]"

there are a lot of detection functions, hook them. This first wildcard matches either - for an instance method or + for a class method. the second * means match all classes.
so, the full query *[* Jailb*] breaks down as:
*(first one): Match all instance (-) and class (+) methods.[: Literal open bracket.*: Match any class.]: Literal close bracket.Jailb*: Match any method name that starts with “Jailb”.
var resolver = new ApiResolver('objc');
resolver.enumerateMatches('*[* Jailb*]', {
onMatch: function (match) {
let funcName = match.name;
let funcAddr = match.address;
Interceptor.attach(ptr(funcAddr),{
onEnter: function (args) {},
onLeave: function (retval) {
if (retval.toInt32() === 1) {
retval.replace(0);
}
console.log(funcName, retval);
}
});
},
onComplete: function () {}
});
resolver.enumerateMatches('*[* JailB*]', {
onMatch: function (match) {
let funcName = match.name;
let funcAddr = match.address;
Interceptor.attach(ptr(funcAddr), {
onEnter: function (args) {},
onLeave: function (retval) {
console.log(funcName, retval);
}
});
},
onComplete: function () {}
});
resolver.enumerateMatches('*[* jailB*]', {
onMatch: function (match) {
let funcName = match.name;
let funcAddr = match.address;
Interceptor.attach(ptr(funcAddr), {
onEnter: function (args) {},
onLeave: function (retval) {
console.log(funcName, retval);
}
});
},
onComplete: function () {}
});
// frida -U -f com.gemd.iting -l hook_muti_functions.js
connect iphone by ssh
ssh is similar to adb, it connects window with ios
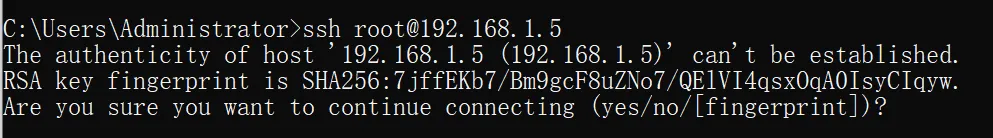
if type yes, next time even if it’s the same ip address but a difference SHA256, it will raise middle attack (?)
default password alpine
other user
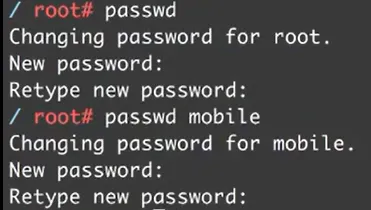
ssh mobile@192.168.1.5(iphone ip address)
change password
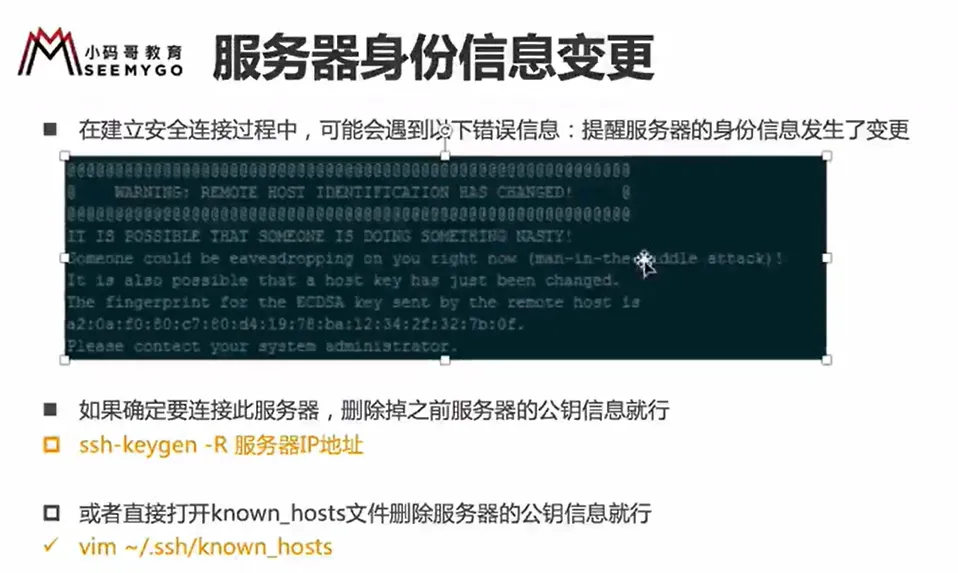
server ip changed it shows man-in-middle attack
delete rsa key in PC
vim know_hosts
move the cursor to the fine row, typedd to delete this row
pushEsc and type :wq
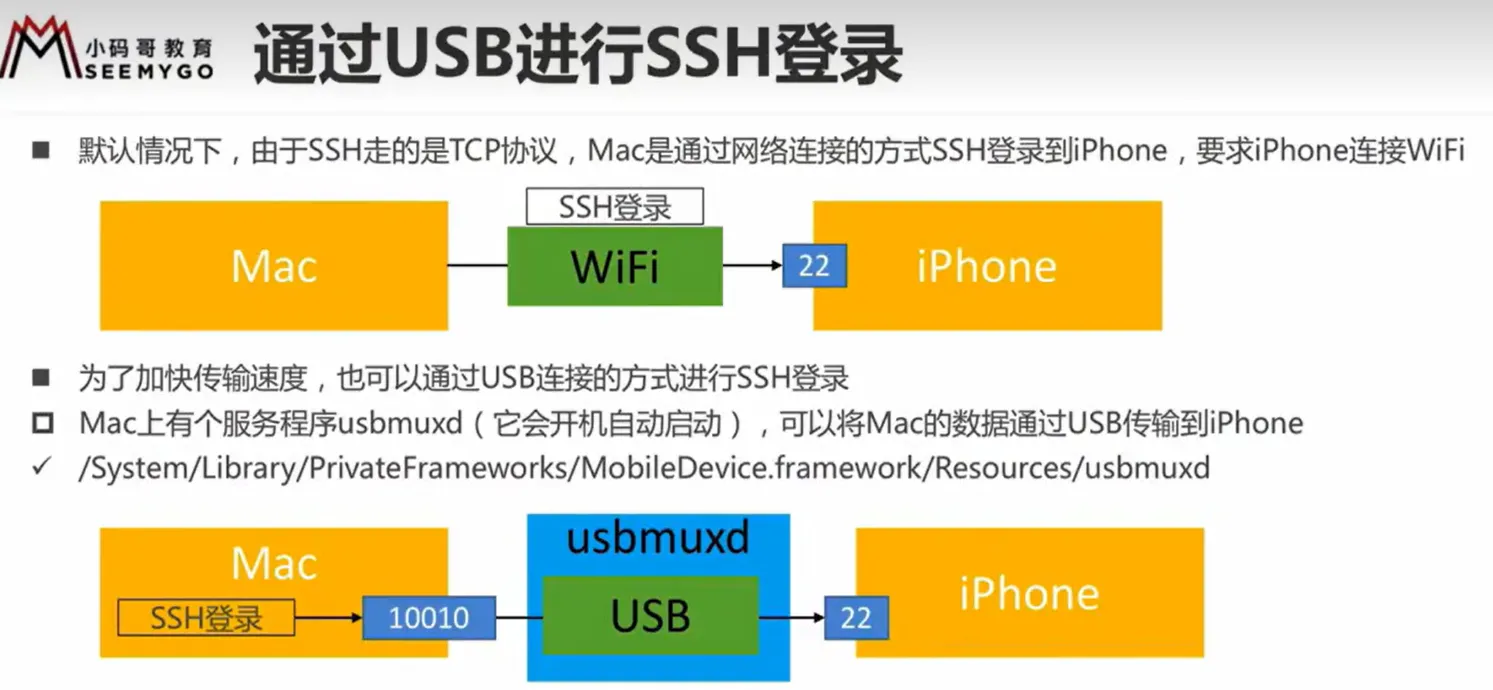
in the latest ios 15.8.1 on iphone 6s
if you cant directly connect root account, it will show shit like “authority failed”. here’s the alternative approach
connect with user
ssh mobile@192.168.1.7input mobile password, the default password is
alpine, but i changed it into1234after inputting the correct password, it will show
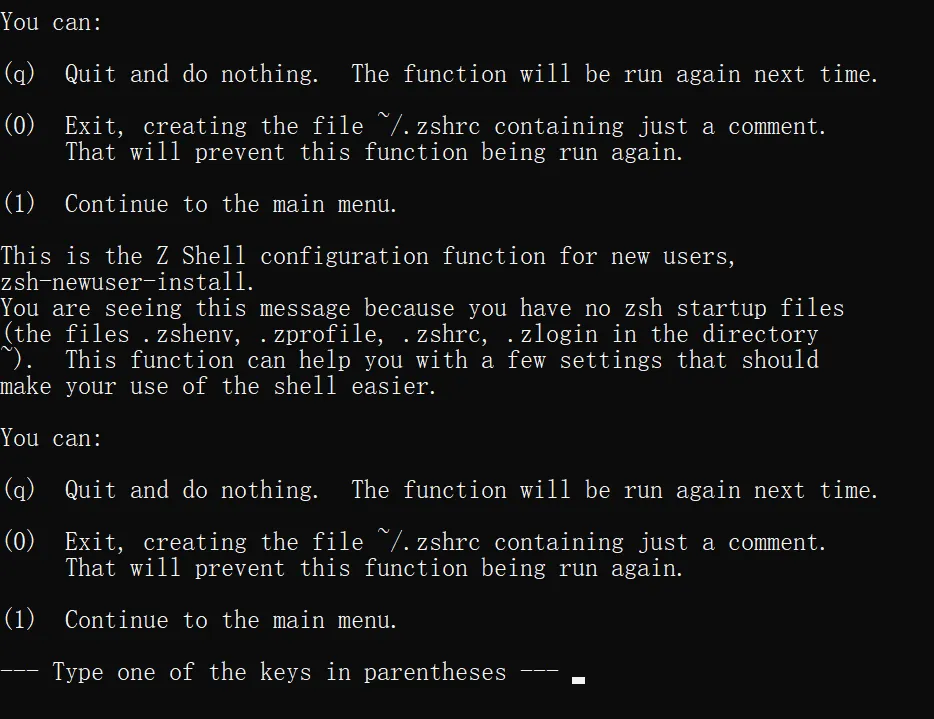
press any button, type
su rootor justsu(I guess both are fine)input root password, mine is
alpine
basic knowledge
iOS Common Directories
- /bin: Stores user-level binary files, such as
cat,chmod,chown. - /dev: Stores device files.
- /etc: Stores system scripts and configuration files, such as
passwd,hosts. This directory actually points to /private/etc. - /sbin: Stores system-level binary files, such as
mount,dmesg. - /tmp: Stores temporary files. This directory actually points to /private/var/tmp.
- /usr/lib: Stores various dylib dynamic libraries.
- /usr/include: Standard C header files.
- /usr/bin: Stores user-installed binary files. Commands for
ssh,dpkg, and Cydia are typically located here. - /var: Contains logs, user data, temporary files, App Store Apps, and the
/var/checkra1n.dmg. - /var/root
- /var/mobile
iOS Directory Descriptions
- /Applications: All system apps and apps installed from Cydia.
- /Developer: Xcode development-related files and tools.
- /Library: Stores data that provides system support.
- /Library/MobileSubstrate/DynamicLibraries: Stores Cydia Substrate plugins.
- /System: Stores a large number of system components and frameworks.
- /System/Library/Frameworks: The location of frameworks like Foundation.framework.
- /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks
- /System/Library/CoreServices: Contains core services like the SpringBoard.app.
- /User: Actually points to /var/mobile, storing user data (photos, text messages, recordings).
- /User/Media
- /var/containers/Bundle/Application/xxxx/DoDoNew.app/: App Store app directory.
- /var/mobile/Containers/Data/Application/xxxx: App data directory (sandbox directory).
The command grep -ril DoDoNew ./* is a command-line utility used to search for a string recursively within files.
pwd show the absolute path of the current path
decrypt an ipa
CrackerXI is a cracking tool that runs on the phone.
The most common way to get an ipa package for an app is by cracking it.
This is because sometimes apps aren’t downloaded from the app store, such as when they are installed via a provisioning profile. In these cases, you must crack the app to get the package.
frida-ios-dump sometimes gets stuck.
- crackerXI https://onejailbreak.com/blog/crackerxi/repository (recommend)
- DumpDecrypter
scp root@192.168.1.4:/var/mobile/Documents/DumpDecrypter/xxx.ipa ./ # move a file from iphone to windows
- frida-ios-dump
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xWQaYMEhs/
https://github.com/AloneMonkey/frida-ios-dump#
dump.py -l # see the app list
Common Classes
NSFileManager
sometimes it is used to detect specific jailbreak files in system.
NSFileManager is created as a singleton. You can get an instance by calling the class method
defaultManager.NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];Common Methods
Determine if a specified file/directory exists
-(BOOL)fileExistsAtPath:(NSString *)path;
Determine if a specified file/directory exists, and check if it is a directory
-(BOOL)fileExistsAtPath:(NSString *)path isDirectory:(BOOL *)isDirectory;
Get all file and directory names in a specified directory
-(NSArray *)subpathsAtPath:(NSString *)path;
Get all file and directory names in a specified directory, not including subdirectories
-(NSArray *)contentsOfDirectoryAtPath:(NSString *)path error:(NSError **)error;
:star2: frida API :star_of_david:
Actively calling a OC method
var nsstr = ObjC.classes.NSString;
var ocstr = nsstr.stringWithFormat_("11111");
console.log(ocstr);
modify params and retval
use $className to see its class.
:smiling_imp: frida address vs IDA address :shit:
defineHandler({
onEnter(log, args, state) {
let urlString = ObjC.Object(args[2]).toString();
if (urlString.indexOf("?sign=") !== -1) {
const backtrace = Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE);
// Get the main application module using a more robust method
const driverModule = Process.getModuleByName('Driver');
const idaBase = new NativePointer('0x100000000');
// A safety check in case the module isn't found
if (!driverModule) {
log('Error: Could not find the "Driver" module. Aborting calculation.');
return;
}
const driverEndAddress = driverModule.base.add(driverModule.size);
// --- Summary Box ---
const topFunctionAddress = backtrace[0];
const topIdaAddress = idaBase.add(topFunctionAddress.sub(driverModule.base));
console.log("\n==================================================");
console.log("[+] Found URL: " + urlString.slice(0, 100) + "...");
console.log(`[✅] Top function call (in IDA): ${topIdaAddress}`);
console.log("==================================================");
// --- Custom Backtrace Formatting with reliable range check ---
const formattedBacktrace = backtrace.map(function(addr) {
const symbol = DebugSymbol.fromAddress(addr);
// **THE FIX**: Check if the address is within the Driver module's memory range
const isAppCode = addr.compare(driverModule.base) >= 0 && addr.compare(driverEndAddress) < 0;
if (isAppCode) {
// It's in our app, so calculate the IDA address
const offset = addr.sub(driverModule.base);
const idaAddress = idaBase.add(offset);
return `${idaAddress} Driver!${symbol.name}`;
} else {
// It's a system library, so find its module and show the runtime address
const otherModule = Process.getModuleByAddress(addr);
const moduleName = otherModule ? otherModule.name : 'UnknownModule';
return `${addr} ${moduleName}!${symbol.name}`;
}
}).join('\n');
log('Backtrace (with calculated IDA addresses):\n' + formattedBacktrace + '\n');
}
},
onLeave(log, retval, state) {}
});
The tutorial I watched used Frida 14.2.8, but I’m on Frida v16.2.5. I believe these version differences are causing the backtrace behavior to change. The tutorial’s method of simply copying an address and jumping to it in IDA doesn’t work for me; instead, I need to perform a calculation to find the correct jump address. For a detailed example of the calculation mentioned, you can refer to the provided link: https://zycreverse.netlify.app/posts/iosjiaxiao/
You’ve run into a very common and important concept when combining runtime analysis (Frida) with static analysis (IDA). The issue is twofold: a memory address mismatch due to ASLR, and as a result, trying to decompile from the middle of an unrelated function.
Here’s what’s happening and how to fix it.
1. The Address Mismatch: Runtime vs. Static Address (ASLR)
The core problem is that the address you see in Frida is not the same as the address in IDA.
- IDA Address (Static): When you load an application into IDA, it assumes a default “base address” for the code, which for 64-bit iOS apps is typically
0x100000000. All function addresses are calculated from this static base. - Frida Address (Runtime): When an app actually runs on your phone, the operating system uses Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) as a security measure. It loads the app into memory at a random base address each time. The address Frida shows you (
0x101ccb374) is the runtime address, which includes this random offset (often called the “ASLR slide”).
You cannot simply copy the Frida address and paste it into IDA. You need to calculate the correct static address.
How to Find the Correct Address in IDA
The formula is simple: IDA Address = IDA Base + (Frida Address - Frida Base)
Here are the steps to find the correct location:
Step 1: Get the Module’s Runtime Base Address in Frida
While your app is running, use this Frida command to find out where the main Driver module was loaded in memory.
Bash
frida -U -N com.jiaxiao.driveAPP -e "console.log('Driver base address: ' + Module.findBaseAddress('Driver'))"
Let’s imagine the output is something like this (your value will be different):
Driver base address: 0x101c00000
Step 2: Calculate the Offset
Now, subtract this runtime base address from the function address you got in your backtrace. This gives you the function’s static offset from the start of the module.
- Frida Function Address:
0x101ccb374 - Frida Module Base Address (Example):
0x101c00000 - Offset:
0x101ccb374 - 0x101c00000 = 0xcb374
This offset (0xcb374) is the “true” location of the function relative to the start of the binary. It will not change between app launches.
Step 3: Calculate the Address in IDA
Finally, add this offset to IDA’s base address for the module (0x100000000).
- IDA Base Address:
0x100000000 - Offset:
0xcb374 - Correct IDA Address:
0x100000000 + 0xcb374 = 0x1000cb374
Now, in IDA, press G (for “Go to”) and enter 0x1000cb374. This will take you to the correct starting instruction of the -[AFHTTPRequestSerializer requestBySerializingRequest:withParameters:error:] function.
2. Why ‘F5’ Decompilation Failed
The reason F5 did nothing is directly related to the address mismatch.
- The Hex-Rays decompiler (
F5) can only decompile a full function. It must start at the function’s very first instruction (the “prologue”). - Because of the ASLR issue, when you jumped to
0x101ccb374in IDA, you landed in the middle of a completely different function (-[BaiduMobAdBookmarkContainerView backgroundView]). - The decompiler saw that
0x101ccb374was not the start of a function and therefore couldn’t do anything.
Once you follow the steps above and jump to the correct calculated address (0x1000cb374 in our example), you will be at the beginning of the correct function, and F5 will work perfectly.
CCCrypt
In the realm of iOS reverse engineering, CCCrypt is a fundamental function that frequently becomes a focal point for analysis. It resides within Apple’s CommonCrypto library, a low-level framework that provides cryptographic operations. Understanding and inspecting CCCrypt is crucial for security researchers and developers alike, as it underpins the encryption and decryption of data in a vast number of iOS applications.
What is CCCrypt and the CommonCrypto Library?
The CommonCrypto library offers a C-level API for a variety of cryptographic tasks. At its core, the CCCrypt function provides symmetric-key encryption and decryption. This means the same key is used for both encrypting and decrypting data.
The function itself has the following signature:
CCCryptorStatus CCCrypt(
CCOperation op, // kCCEncrypt or kCCDecrypt
CCAlgorithm alg, // Algorithm (e.g., kCCAlgorithmAES)
CCOptions options, // Options (e.g., kCCOptionPKCS7Padding)
const void *key, // The encryption key
size_t keyLength, // Length of the key
const void *iv, // Initialization Vector (optional)
const void *dataIn, // Input data to be processed
size_t dataInLength, // Length of the input data
void *dataOut, // Buffer for the output data
size_t dataOutAvailable, // Size of the output buffer
size_t *dataOutMoved // On return, the number of bytes written
);
Reverse engineers pay close attention to this function because it’s where sensitive information is often handled. By intercepting calls to CCCrypt, one can gain insight into how an application protects its data, what data is being protected, and potentially uncover vulnerabilities in the implementation.
Why is CCCrypt a Prime Target in Reverse Engineering?
Applications use CCCrypt for a wide range of purposes, from securing user credentials and encrypting local files to protecting communication with a server. For a reverse engineer, analyzing these calls can reveal:
- Hardcoded Keys: Developers sometimes embed encryption keys directly within the application’s code. By tracing the
keyparameter ofCCCrypt, these keys can often be extracted. - Weak Algorithms or Modes: An application might use an outdated or insecure encryption algorithm or mode of operation. For example, using ECB mode is generally discouraged as it can reveal patterns in the encrypted data.
- Static Initialization Vectors (IVs): The use of a static or predictable IV can significantly weaken the encryption.
- Sensitive Data in Plaintext: By examining the
dataInanddataOutbuffers, a reverse engineer can see the data before encryption and after decryption, potentially exposing sensitive user information, API keys, or proprietary data.
Analyzing CCCrypt with Frida
Frida is an indispensable tool for iOS reverse engineering, allowing for the dynamic instrumentation of running applications. With Frida, you can hook into the CCCrypt function and inspect its arguments in real-time.
var encrypt_func = Module.findExportByName("libcommonCrypto.dylib", "CCCrypt");
Interceptor.attach(encrypt_func, {
onEnter: function (args) {
console.log("[+] CCCrypt function called");
console.log("[+] CCOperation: " + args[0].toInt32());
console.log("[+] CCAlgorithm: " + args[1].toInt32());
console.log("[+] CCOptions: " + args[2].toInt32());
console.log("[+] key: \n" + hexdump(ptr(args[3]), { length: args[4].toInt32() }));
console.log("[+] keyLength: \n" + args[4].toInt32());
console.log("[+] iv: \n" + hexdump(ptr(args[5]), { length: 16 }));
console.log("[+] dataIn: \n" + hexdump(ptr(args[6]), { length: args[7].toInt32() }));
console.log("[+] dataInLength: " + args[7].toInt32());
this.dataOutPtr = args[8];
this.dataOutLengthPtr = args[10];
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
console.log("[+] dataOut: \n" + hexdump(ptr(this.dataOutPtr), { length: ptr(this.dataOutLengthPtr).readUInt() }));
}
});
UI related knowledge
Checking the function of UI controls You can locate key code by using UI controls. It can distinguish whether an app is native or H5. The reverse engineering methods for apps developed in different forms are not the same. Most of the encryption for H5 apps is in JS, but a very small number of apps are in Objective-C (OC), or a mixture.
Introduction to Reveal Disadvantages:
- Not free
- Can only be used on Mac
- Configuration is relatively troublesome Advantages:
- Displays the UI more intuitively
**Frida to print UI ** https://github.com/teapot-4l8/FridaDev
use frida to list all bundle id
import frida
device = frida.get_usb_device()
session = device.attach("SpringBoard")
script = session.create_script("""
if (ObjC.available) {
var workspace = ObjC.classes.LSApplicationWorkspace.defaultWorkspace();
var apps = workspace.allInstalledApplications();
for (var i = 0; i < apps.count(); i++) {
var app = apps.objectAtIndex_(i);
try {
var name = app.localizedName();
var bundleId = app.applicationIdentifier();
console.log(name.toString() + " : " + bundleId.toString());
} catch (e) {}
}
}
""")
script.load()
use frida-ps -Uai to check out name
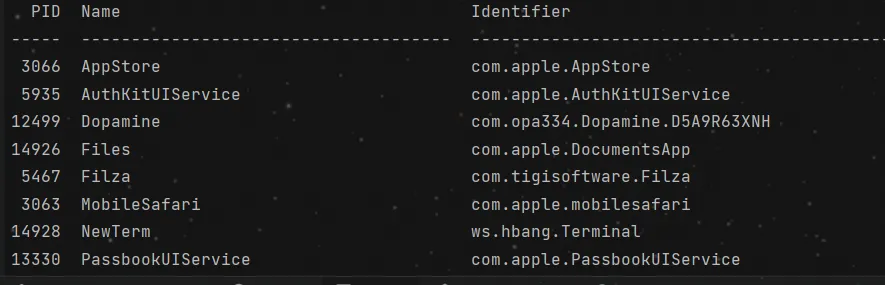
and use the name of app to print UI python fridaDev.py -u [Name]
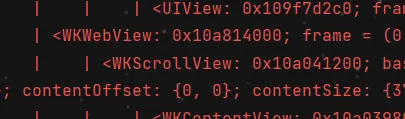
if you see webview, that app is made of a web. in www/ file, it have index.html
ps aux |grep [Name]
scp -r root@192.168.1.4:[xx/xx/x/xxx] [t]

Hook: Substitute VS ElleKit
The difference between Substitute and ElleKit in iOS Jailbreaking
If you’re using Dopamine, which is a rootless jailbreak, the default injection framework on your device is likely ElleKit, not Substitute.
- Dopamine is a modern, rootless jailbreak tool that supports devices with A12 chips and newer. It’s compatible with iOS versions ranging from 15.0 to 16.6.1 (though the specific support list may change).
- ElleKit is the code injection and hooking framework specifically designed for rootless jailbreaks. Its core function is similar to Substitute’s—modifying an app’s behavior at runtime—but it’s built to work within the rootless jailbreak environment.
The main difference between a rootless jailbreak and a traditional rootful one is that a rootless jailbreak installs all its files in the /var directory instead of directly modifying the root filesystem (/). This design makes the jailbreak more secure and easier to remove.
Because of this architectural difference, traditional hooking frameworks like the rootful version of Substitute can’t work directly in a rootless environment. That’s why rootless jailbreak tools like Dopamine use ElleKit as their default injection framework.
So, when you’re doing reverse engineering on a device with a Dopamine rootless jailbreak, you should be focusing on tools and tweaks that are compatible with ElleKit, not Substitute. Most modern tweak developers ensure compatibility with both frameworks, but some very old tweaks might only support Substitute.
locate the relevant function
URLWithString
defineHandler({
onEnter(log, args, state) {
// args[0] is 'self', args[1] is the selector 'URLWithString:', args[2] is the string argument
let urlString = ObjC.Object(args[2]).toString();
// Check if the URL string contains the desired substring
if (urlString.indexOf("verifycode_login?sign") !== -1) {
console.log("Found URL containing 'verifycode_login?sign': " + urlString);
// Log the backtrace to see where the call originated from
console.log('Backtrace:\n' +
Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE)
.map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join('\n') + '\n');
}
},
onLeave(log, retval, state){}
})
// frida-trace -U -N cn.xiaochuankeji.tieba -m "+[NSURL URLWithString:]"
UIAlertView
initWithTitle_message_delegate_c_9aad7c17.js
defineHandler({
onEnter(log, args, state) {
log('UIAlertView initWithTitle called from:\n' +
Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE)
.map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join('\n') + '\n');
log(`-[UIAlertView initWithTitle:${args[2]} message:${args[3]} delegate:${args[4]} cancelButtonTitle:${args[5]} otherButtonTitles:${args[6]}]`);
},
onLeave(log, retval, state) {
}
});
// frida-trace -UF -m "*[UIAlertView *]"
Cryptography
Hex Encoding Features
Uses 16 characters from 0-9 and a-f for representation.
Each hexadecimal character represents 4 bits, so two hexadecimal characters represent one byte.
In practical applications, such as key initialization, it is crucial to clarify which encoding the transmitted key uses and to use the corresponding method for parsing to get the correct result.

Base64

md5
There are two ways to write the MD5 algorithm.

When using this :point_down: method, note that when you hook it, you’ll get the plaintext from the str in CC_MD5_Update, and the result from CC_MD5_Final.

SHA1

Hmac
The difference between the Hmac algorithm and MD/SHA is the addition of a key, which can be provided randomly.
The byte array after encryption can be encoded into Hex or Base64.

ATTENTION
- The encrypted byte array can be encoded as Hex or Base64
- To reverse a symmetric encryption algorithm, you need to get the plaintext, key, iv, mode, and padding.
- The plaintext, key, and iv need to be parsed carefully and are not necessarily in string format.
- If the encryption mode is ECB, the iv is not needed.
- If there are two identical content blocks in the plaintext, ECB will produce identical ciphertext, while CBC will not.
- The result of an encryption algorithm is usually the same length as the plaintext or longer. If it becomes shorter, it might be due to gzip or protobuf.
DES
CBC mode

ECB mode (don’t need iv)

AES
CBC mode

ECB

![]()
RSA
![RSA1][ios_reverse.assets/RSA1.png]
RSA Modes and Padding
a) NoPadding - Maximum number of plaintext bytes equals the key size. - The ciphertext and key sizes are equal. - The ciphertext is padded with zero bytes and does not change after encryption.
b) pkcs1padding - Maximum number of plaintext bytes equals the key size minus 11. - The ciphertext and key sizes are equal. - The padding for each encryption is different, causing the ciphertext to change after each encryption.
Common combinations of multiple encryption algorithms
- randomly generate AES key
- AES key is used for AES encryption of data, resulting in ciphertext.
- RSA is used for AES key encryption, resulting in encrypted ciphertextKey.


develop extensions (tweaks)
system: Ubuntu 20.04
Theos: https://theos.dev/docs/
add nic.pl to path
Clean up the previous incorrect lines:
First, you need to remove the incorrect lines you added to your .bashrc file. You can open the file with a simple editor like nano.
Bash
nano ~/.bashrcIn the file, find and delete the two lines you previously added.
Add the correct environment variables:
At the end of the file, add these two correctly configured lines:
Bash
export THEOS=/aaa/theos export PATH="$THEOS/bin:$PATH"Note that on the second line, we use the
exportkeyword to ensure thePATHvariable is available to sub-processes. We also use double quotes" "to ensure the$THEOSvariable will be correctly expanded when the file is sourced, not when theechocommand is run.Save and exit:
In the nano editor, press Ctrl + O to save the file, then press Enter to confirm the filename. Next, press Ctrl + X to exit the editor.
Apply the changes immediately:
You don’t need to close and reopen your terminal. Run the following command to load the new .bashrc configuration:
Bash
source ~/.bashrcVerify the setup:
Now you can try running the nic.pl command to check if it’s working. If everything is correct, it should display the usage information.
Bash
nic.plYou can also use the
echocommand to verify that theTHEOSandPATHenvironment variables are set correctly:Bash
echo $THEOS echo $PATHIf the output shows
/aaa/theosand/aaa/theos/binin the respective paths, your setup is successful.
cases
[海博tv][./iosHaiboTV.md]
other interesting shit
Share VPN
they should be LAN
ur vpn android device
v2yan: change socks5 and http port as the same number, allow coonections from the LAN
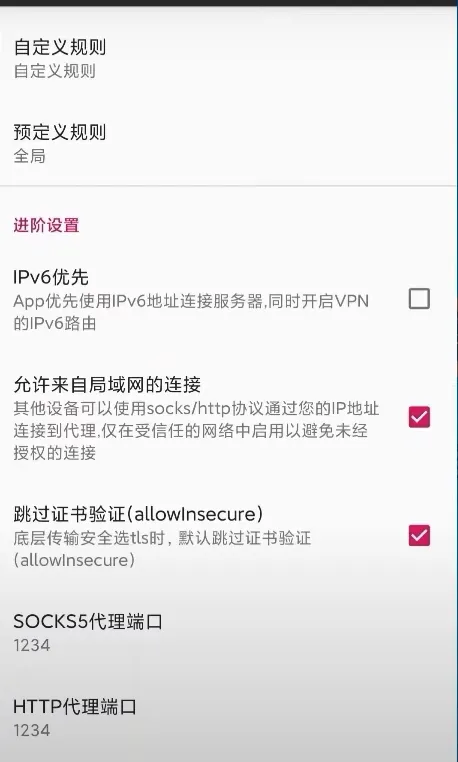
ur vpn not found window device
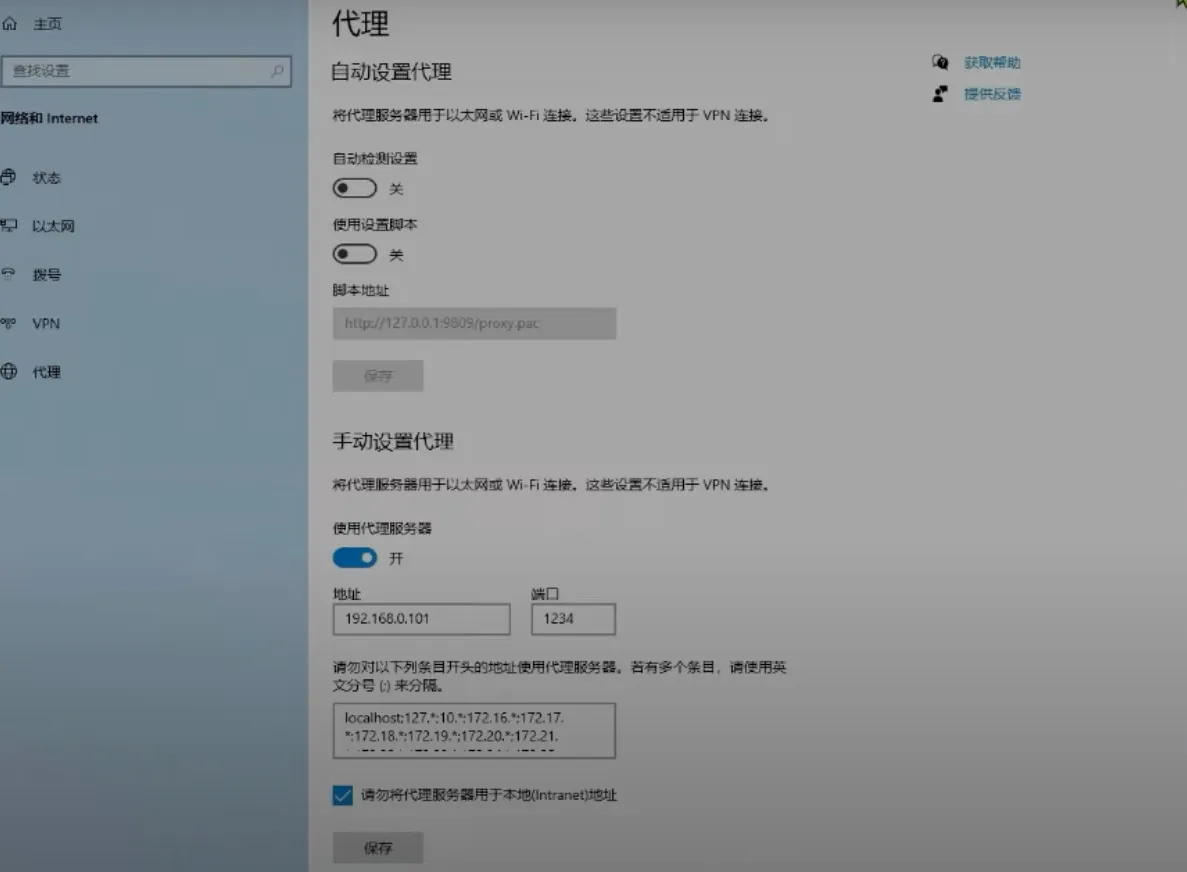
ios
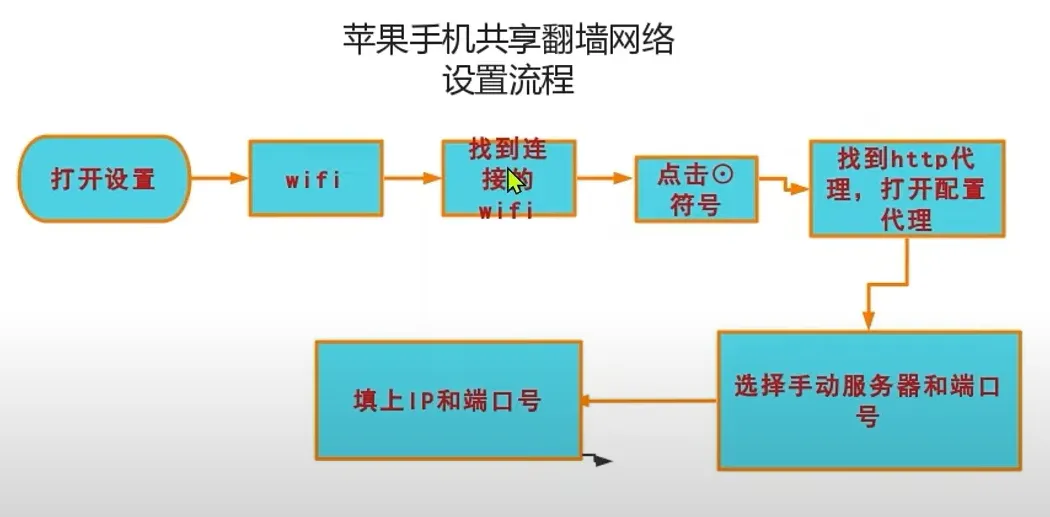
this is clash. also change http and socks port and allow LAN

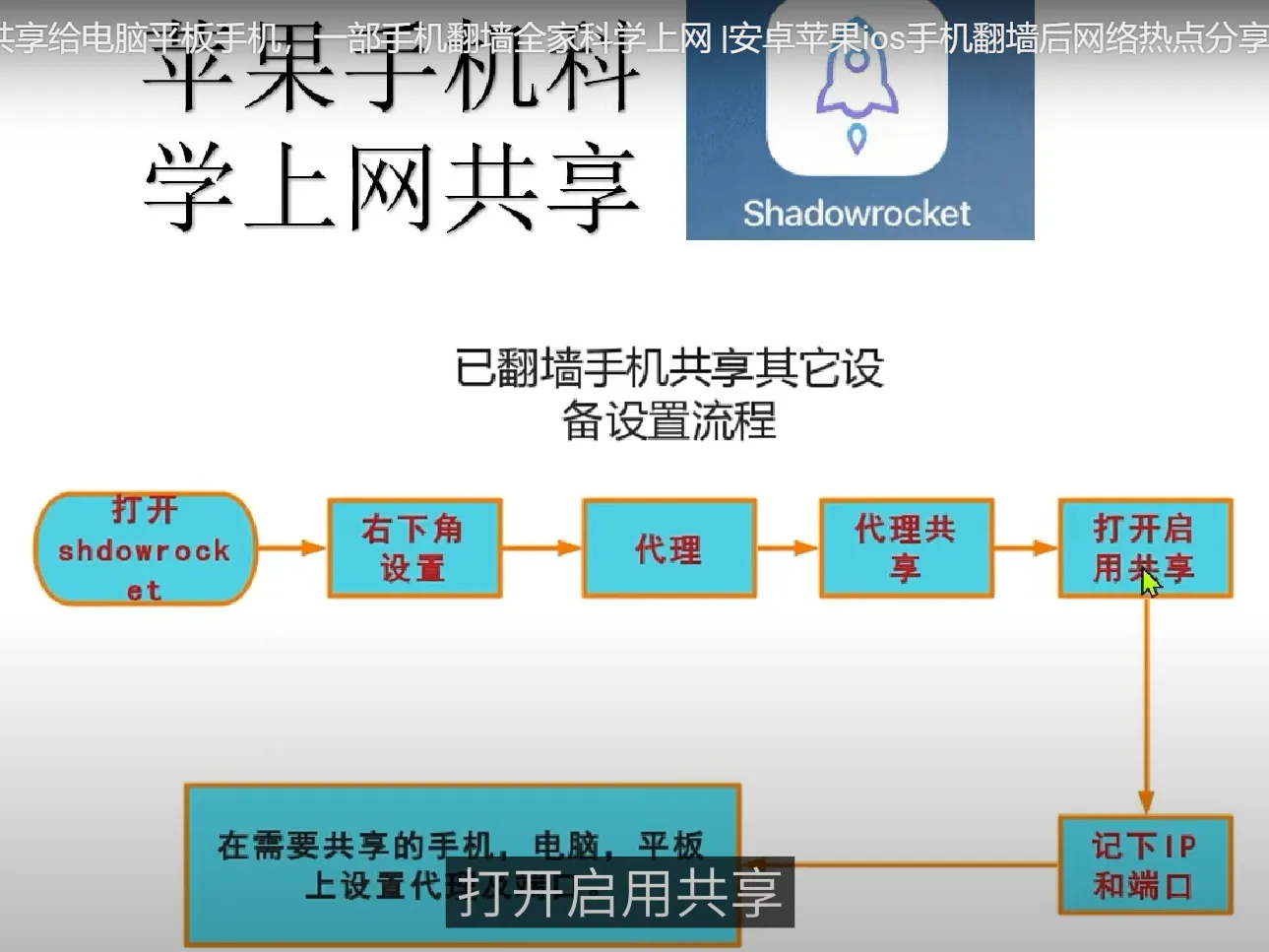
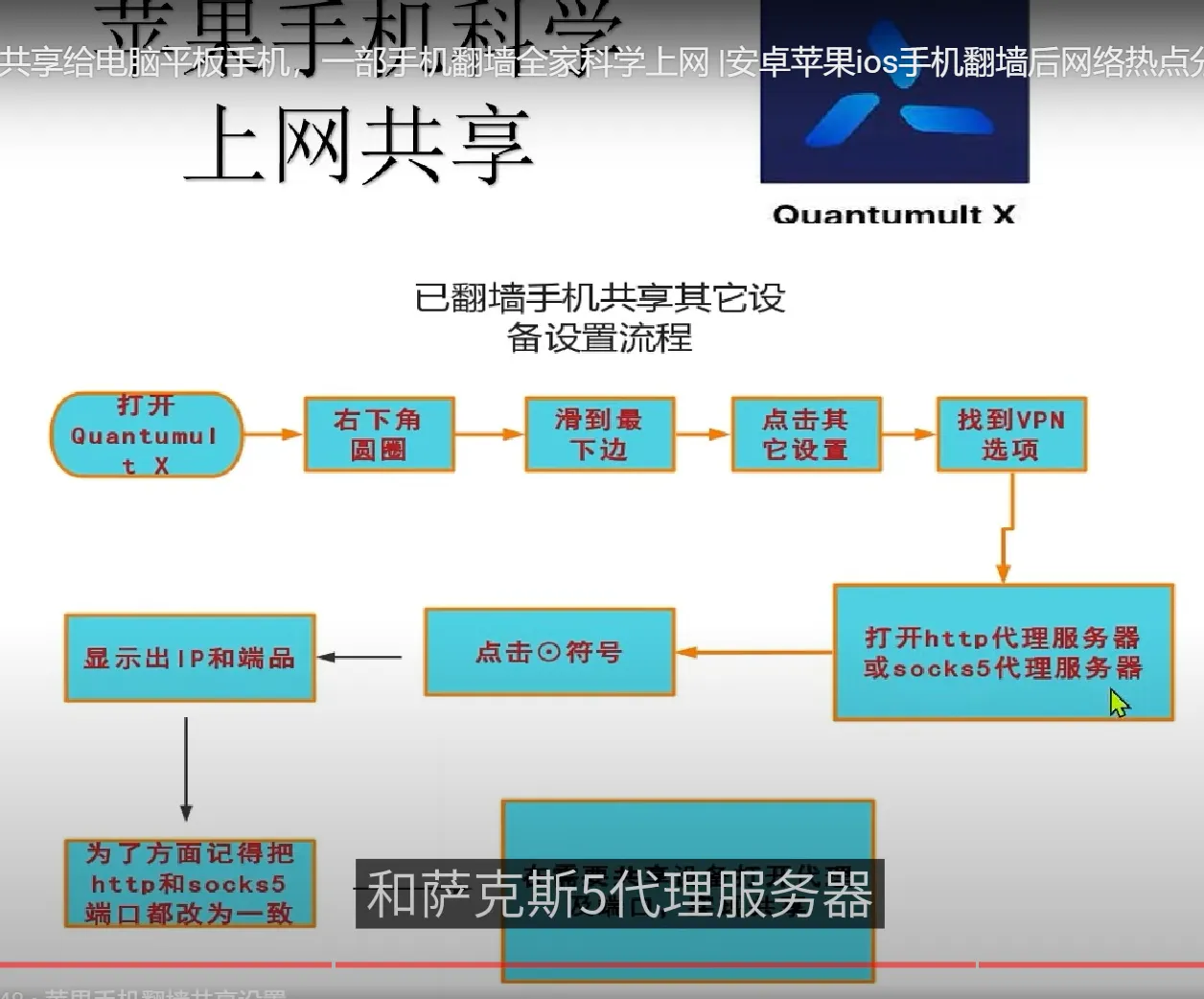
useful address
http://zhaoboy9692.github.io/repo
https://ids.ailiao.eu shared account :+1: :+1: :+1: :+1:
[./iosHaiboTV.md]:
